Laravel Localization
Laravel's localization features provide a convenient way to retrieve strings in various languages, allowing you to easily support multiple languages within your application.
Introduction
Laravel's localization features provide a convenient way to retrieve strings in various languages, allowing you to easily support multiple languages within your application. Language strings are stored in files within the /lang directory. Within this directory there should be a subdirectory for each language supported by the application:
Or, translation strings may be defined within JSON files that are placed within the /lang directory. When taking this approach, each language supported by your application would have a corresponding JSON file within this directory. This approach is recommended for application's that have a large number of translatable strings:
📂 lang
├── 📄 en.json
├── 📄 de.json
├── 📄 ar.json
└── 📄 fr.jsonConfiguring The Locale
The default language for your application is stored in the config/app.php configuration file. You may modify this value to suit the needs of your application.
You may modify the default language for a single HTTP request at runtime using the setLocale method provided by the App facade:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\App;
Route::get('/greeting/{locale}', function ($locale) {
if (! in_array($locale, ['en', 'es', 'fr'])) {
abort(400);
}
App::setLocale($locale);
...
});You may configure a "fallback language", which will be used when the active language does not contain a given translation string. Like the default language, the fallback language is also configured in the config/app.php configuration file:
'fallback_locale' => 'en',Determining The Current Locale
You may use the currentLocale and isLocale methods on the App facade to determine the current locale or check if the locale is a given value:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\App;
$locale = App::currentLocale();
if (App::isLocale('en')) {
...
}Retrieving Translation Strings
You may retrieve lines from language files using the __ helper function. The __ method accepts the file and key of the translation string as its first argument. For example, let's retrieve the welcome translation string from the /lang/en/locale.php language file.
echo __('locale.welcome');If you are using the Blade templating engine, you may use the ❴❴ ❵❵ syntax to echo the translation string or use the @lang directive:
❴❴__('locale.welcome')❵❵
@lang('messages.welcome')Now, all set to work localization in simple project.🥳
Localization In Frest
In Frest, We have a language dropdown for switching the language. You can find it in the navbar. Let's understand how it works.
We have created a controller to check whether a selected language available or not. If selected language is available then save it to session variables. You can find it at app -> Http -> Controllers -> language -> LanguageController.php location.
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers\language;
use App\Http\Controllers\Controller;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\App;
class LanguageController extends Controller
{
public function swap($locale)
{
if (!in_array($locale, ['en', 'fr', 'de', 'ar'])) {
abort(400);
} else {
session()->put('locale', $locale);
}
App::setLocale($locale);
return redirect()->back();
}
}We have defined a Route for language switching in the routes/web.php file.
// locale
Route::get('lang/{locale}', 'App\Http\Controllers\language\LanguageController@swap');We have a middleware that checks and changes the Language globally. You can find it at app -> Http -> Middleware -> LocaleMiddleware.php location.
<?php
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Closure;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
class LocaleMiddleware
{
/**
* Handle an incoming request.
*
* @param \Closure(\Illuminate\Http\Request): (\Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response) $next
*/
public function handle(Request $request, Closure $next): Response
{
// Locale is enabled and allowed to be change
if (session()->has('locale') && in_array(session()->get('locale'), ['en', 'fr', 'de', 'ar'])) {
app()->setLocale(session()->get('locale'));
}
return $next($request);
}
}Here is the code of our language dropdown:
<!-- Language -->
<li class="nav-item dropdown-language dropdown me-2 me-xl-0">
<a class="nav-link dropdown-toggle hide-arrow" href="javascript:void(0);" data-bs-toggle="dropdown">
<span class="align-middle d-sm-inline-block d-none">English</span>
</a>
<ul class="dropdown-menu dropdown-menu-end">
<li>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="❴❴url('lang/en')❵❵" data-language="en" data-text-direction="ltr">
<span class="align-middle">English</span>
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="❴❴url('lang/fr')❵❵" data-language="fr" data-text-direction="ltr">
<span class="align-middle">French</span>
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="❴❴url('lang/ar')❵❵" data-language="ar" data-text-direction="rtl">
<span class="align-middle">Arabic</span>
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="❴❴url('lang/de')❵❵" data-language="de" data-text-direction="ltr">
<span class="align-middle">German</span>
</a>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<!--/ Language -->We have only translated our vertical menu and horizontal menu. You can translate your whole template. You can find our menus at views -> layouts -> sections -> menu location.
We have stored our translation string in lang lang -> en/fr/de/ar.json files.
📂 lang
├── 📄 en.json
├── 📄 de.json
├── 📄 ar.json
└── 📄 fr.jsonHow to add a New Language?
- To add a new language in the whole template, first we need to create a
locale.phpor aJSONfile in thelang/folder. The language file should return an array with key and value pairs. We suggest using a JSON file for store translation as we have used the same. - Now, we need to mention our new language in controller and middleware which we already created.
- Now, you can set your new language as a default language in
config/app.phpfiles
{
"Dashboards": "Tableaux de bord",
"eCommerce": "commerce électronique",
"Layouts": "Dispositions",
"Collapsed menu": "Menu réduit",
"Content navbar": "Barre de navigation du contenu",
"Content nav + Sidebar": "Navigation dans le contenu + barre latérale",
"Navbar full": "Barre de navigation pleine",
"Navbar full + Sidebar": "Navbar complet + Sidebar",
"Horizontal": "Horizontal",
"Vertical": "Vertical",
"Without menu": "Sans menu",
"Without navbar": "Sans barre de navigation",
"Fluid": "Fluide",
}App -> Http -> Controllers -> language -> LanguageController.php
public function swap($locale)
{
if (!in_array($locale, ['en', 'fr', 'de', 'ar'])) {
...
}
}App -> Http -> Middleware -> LocaleMiddleware.php
// Locale is enabled and allowed to be change
if (session()->has('locale') && in_array(session()->get('locale'), ['en', 'fr', 'de', 'ar'])) {
...
}'locale' => 'en',How to remove existing language?
- To remove a existing language in whole template, first we need to delete language file from
langfolder. - Now, you have to remove the language name from the array of language in controller and middleware.
- Finally, Remove the language option from the language dropdown in Navbar.
📂 lang
├── 📄 en.json
├── 📄 de.json
├── 📄 ar.json
└── 📄 fr.jsonApp -> Http -> Controllers -> language -> LanguageController.php
public function swap($locale)
{
if (!in_array($locale, ['en', 'fr', 'de', 'ar'])) {
...
}
}App -> Http -> Middleware -> LocaleMiddleware.php
// Locale is enabled and allowed to be change
if (session()->has('locale') && in_array(session()->get('locale'), ['en', 'fr', 'de', 'ar'])) {
...
}<!-- Language -->
<li class="nav-item dropdown-language dropdown me-2 me-xl-0">
<a class="nav-link dropdown-toggle hide-arrow" href="javascript:void(0);" data-bs-toggle="dropdown">
<span class="align-middle d-sm-inline-block d-none">English</span>
</a>
<ul class="dropdown-menu dropdown-menu-end">
<li>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="❴❴url('lang/en')❵❵" data-language="en" data-text-direction="ltr">
<span class="align-middle">English</span>
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="❴❴url('lang/fr')❵❵" data-language="fr" data-text-direction="ltr">
<span class="align-middle">French</span>
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="❴❴url('lang/ar')❵❵" data-language="ar" data-text-direction="rtl">
<span class="align-middle">Arabic</span>
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="❴❴url('lang/de')❵❵" data-language="de" data-text-direction="ltr">
<span class="align-middle">German</span>
</a>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<!--/ Language -->Localization In Template Customizer
We have also provided Localization in our Template Customizer. We have not handled Customizer's locale through Laravel but it is slightly interconnected.
When you change the template language using language dropdown from navbar. It'll also change the template customizer's language as per the selected language.
Internally, we have created a variable that is set as per the current laravel language and sent this variable to our template-customizer.js file where we handle the customizer's localization.
Let's deep dive into it and understand how it works.
Internal variable to set Template Customizer's localization.
<script>
window.templateCustomizer = new TemplateCustomizer({
lang: '❴❴ app()->getLocale() ❵❵',
...
});
</script>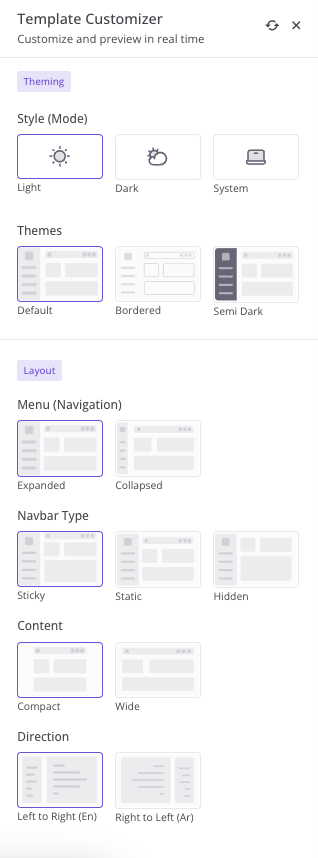
We have a javascript object of languages where you have to put your translation for customizer in template-customizer.js file.
// Theme setting language
TemplateCustomizer.LANGUAGES = {
en: {
panel_header: 'Template Customizer',
panel_sub_header: 'Customize and preview in real time',
theming_header: 'Theming',
style_label: 'Style (Mode)',
theme_label: 'Themes',
layout_header: 'Layout',
layout_label: 'Menu (Navigation)',
layout_header_label: 'Header Types',
content_label: 'Content',
layout_navbar_label: 'Navbar Type',
direction_label: 'Direction'
},
fr: {...},
de: {...},
ar: {...}
}If you add or remove any language in Laravel then you have to add or remove the same language from the above Object. Otherwise, you'll get console errors.
If you don't want to use localization for customizer then you need to remove lang option from scriptsIncludes.blade.php file:
<script>
window.templateCustomizer = new TemplateCustomizer({
lang: '❴❴ app()->getLocale() ❵❵',
...
});
</script>